Social Sciences Glossary
The World and the Society.
Hi, my name is Mia Chevrette, and I am a student in Social Sciences profile world and society. I study the environment that we live in such as his past and present civilizations and his general problematic. The purpose of this glossary is to help students in same field as me to better understand terms associated to the Social Sciences by giving there definition.
- society
- noun
- The community of people living in a particular country or region and having shared customs, laws, and organizations.
- Example: Our point is that a popular movement such as the peace movement carries within itself a notion of a just society and that law cannot be considered merely as a "tool" isolated from broader political and social considerations.
- fr: société

- politics
- noun
- The activities associated with the governance of a country or other area, especially the debate or conflict among individuals or parties having or hoping to achieve power.
- Example: This dissertation explores the impact of World War I on British society through politics, design, and construction of state-funded housing in Birmingham, England during the inter-war period.
- fr: politique

- democracy
- noun
- A system of government by the whole population or all the eligible members of a state, typically through elected representatives.
- Example: The prospect for democracy in Africa is the central concern of this study.
- fr: démocratie

- psychology
- noun
- The scientific study of the human mind and its functions, especially those affecting behavior in a given context.
- Example: What were the implications of cognitive psychology for education?
- fr: psychologie
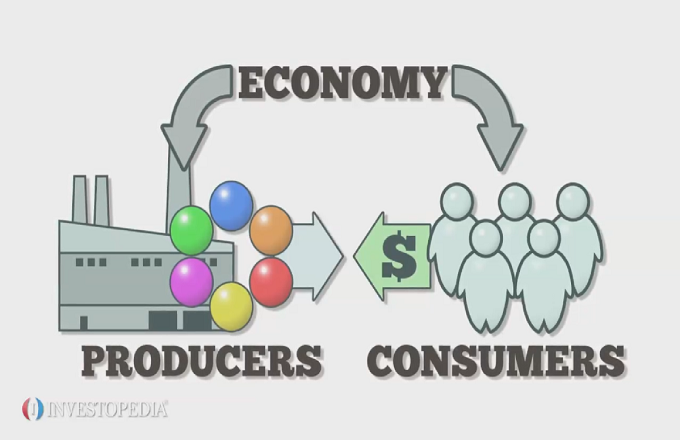
- economy
- noun
- An economy is a system of making and trading things of value. It is usually divided into goods (physical things) and services (things done by people). It assumes there is medium of exchange, which in the modern world is a system of finance. This makes trade possible.
- Example: In the late 1990s, the economy of Southeast Asia sank into recession.
- fr: économie
- geography
- noun
- Geography is the study of places and the relationships between people and their environments.
- Example: Yet, realist methodologies are underdeveloped and poorly understood in the field of geography, which limits geographers' ability to translate their dynamic theories of the social world into as equally dynamic research in practice.
- fr: géographie

- environment
- noun
- The surroundings or conditions in which a person, animal, or plant lives or operates.
- Example: So with a better knowledge of English i'll be able to do my work properly since the English environment won't be a threat to me anymore.
- fr: environnement

- anthropology
- noun
- Anthropology is the study of what makes us human.They consider the past, through archaeology, to see how human groups lived hundreds or thousands of years ago and what was important to them. They consider what makes up our biological bodies and genetics, as well as our bones, diet, and health.
- Example: If my English was better it would give me the chance to work abroad in foreign contries I studied three semesters in anthropology at and I found out that I could not make a career into it without improving my English.
- fr: Anthropologie

- history
- noun
- History is the study of change over time, and it covers all aspects of human society.
- Example: Because i'm presently in second year as a geography and history high school teacher, i won't use English a lot a work.
- fr: histoire

- globalization
- noun
- Globalization means the speedup of movements and exchanges (of human beings, goods, and services, capital, technologies or cultural practices) all over the planet. One of the effects of globalization is that it promotes and increases interactions between different regions and populations around the globe.
- Example: Today, with the globalization of the markets, you have to be able to talk a different languages.
- fr: mondialisation
- sociocultural
- adjective
- The definition of sociocultural is something that involves the social and cultural aspects.
- Example: It is found that gender role bias has played an uncomfortably large part in Iron Age scholarship, and that outdated sociocultural assumptions continue to foster an unstoppable view of elements of world history.
- fr: socioculturel

- humanism
- noun
- An outlook or system of thought attaching prime importance to human rather than divine or supernatural matters. Humanist beliefs stress the potential value and goodness of human beings, emphasize common human needs, and seek solely rational ways of solving human problems.
- Example: The rebirth of the visual arts was one aspect of the Renaissance but the development of humanism and the classical studies of the universities were as important.
- fr: humanisme

- organization
- noun
- An organization is an entity – such as a company, an institution, or an association – comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.
- Example: Several years later, I am now working in an canadian organization dealing with international development.
- fr: organisation

- individual
- noun
- An individual is that which exists as a distinct entity. Individuality (or self-hood) is the state or quality of being an individual; particularly of being a person separate from other people and possessing their own needs or goals, rights and responsibilities.
- Example: In other words: the basis enchance the ability to get a conversation, with a group or an individual, to a second level.
- fr: individu

- media
- noun
- Media is the communication outlets or tools used to store and deliver information or data. The term refers to components of the mass media communications industry, such as print media, publishing, the news media, photography, cinema, broadcasting, digital media, and advertising.
- Example: Most of the media and information available is written in English.
- fr: média

- socialisation
- noun
- The process of learning to behave in a way that is acceptable to society.
- Example: The institutions of socialisation are all modified to take on different roles, so the school takes over some of the functions of the family, and the 'church loses influence being displaced by the printed page.
- fr: socialisation

- myth
- noun
- A traditional story, especially one concerning the early history of a people or explaining some natural or social phenomenon, and typically involving supernatural beings or events.
- Example: This dissertation will analyze the response of contemporary American sculptors to the culture, art, myth and ritual of Native Americans.
- fr: mythe

- culture
- noun
- Culture is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.
- Example: I think the best way to really learn about a new culture is to live there and meet people living there.
- fr: culture

- behavior or behaviour
- noun
- Behavior or is the actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in conjunction with themselves or their environment, which includes the other systems or organisms around as well as the physical environment.
- Example: It is also important to understand that a person's attitude and beliefs can affect behavior and therefore, can influence health as a result (Condon et al, 2003).
- fr: comportement
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/behavioral-psychology-4157183-FINAL-5d8248854be64e34a9f4792179e6c998.png)
- value
- noun
- A person's principles or standards of behavior; one's judgment of what is important in life.
- Example: An analysis of how the traditional values and beliefs of the rural community within George Eliot's Adam Bede create outsiders.
- fr: valeur